Questions and Answers
Here you will find answers to some of the most frequently asked questions in regards to the NEMO project
NEMO technologies target High emitting vehicles in the traffic flow. How do we know, that this is an effective approach?
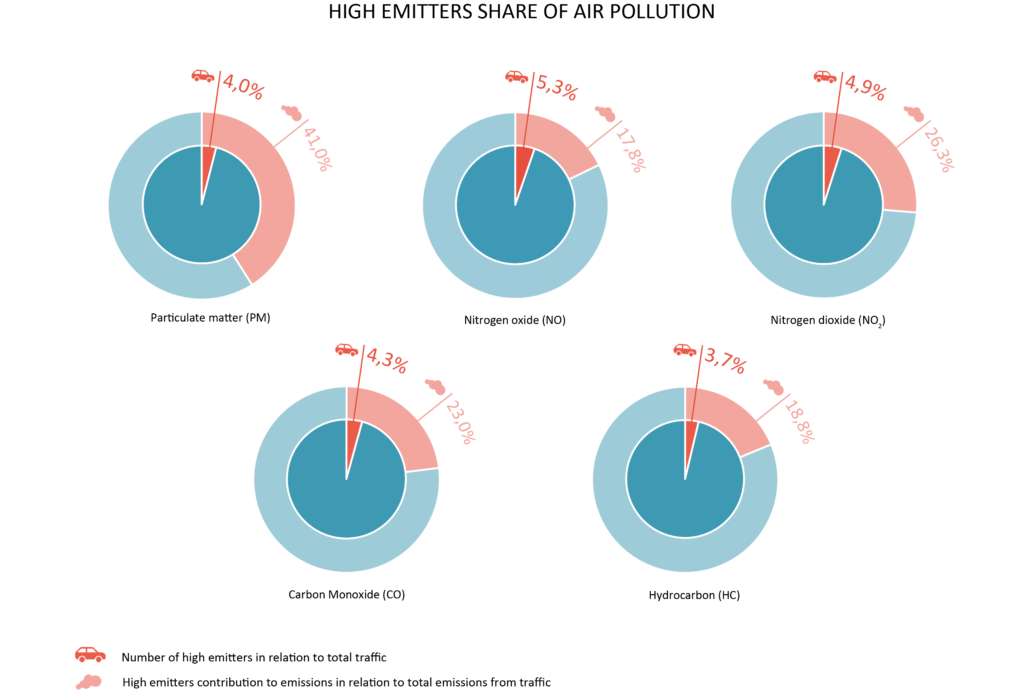
Opus RSE and CIEMAT carried out studies in Madrid using remote sensing technology to identify high emitters. A vehicle was categorized as a high emitter if it was among the top 2% most polluting vehicles). The study showed that a quite a small share of vehicles, vehicles categorized as High Emitters is responsible for a large share of air pollution caused by traffic.
For a vehicle to be categorized as a Emitter it must be among the top 2% most polluting vehicles at least once and among the top 20% most polluting vehicles at least twice. Further at least 70% of the times a vehicle’s pollution level was measured it must be among the top 20% most polluting vehicles. Since emissions from vehicles can vary, this is to avoid a vehicle being falsely identified as a high emitter based on a singular event of high emissions from a vehicle that normally performs well.
Using this method, just 3,7-5,3% of the vehicles were identified as High Emitters, depending on the pollutant. These vehicles were found to be responsible for 17,8-41,0% of the total pollution from traffic.
Thus, targeting and excluding the few High emitters has great potential to improve the air quality in urban areas, for the benefits of all citizens.
Learn more about NEMO’s approach here.
How can E-RSD technology be integrated into existing traffic monitoring systems?
E-RSD technology, which has been significantly improved in the NEMO project, can now operate 24/7 and be integrated into infrastructure, unlike traditional portable systems. This allows for continuous monitoring and can be deployed on 2-lane roads, providing a more comprehensive understanding of emissions without the need for substantial manpower.
Learn more about hte integration here.
What advancements have been made in remote sensing for vehicle emissions?
The NEMO project has developed a new prototype of E-RSD technology that can autonomously monitor emissions from road, sea, and rail vehicles. This device has been validated and tested in various European cities and can measure a range of pollutants including NOx, CO, HC, NH3, SO2, and PM.
Learn more about the progress NEMO has made here.
How does the N-RSD system measure noise emissions from vehicles?
The N-RSD system uses roadside or gantry-mounted microphones to measure noise levels from passing vehicles or trains. This technology relates individual sound levels to each passing vehicle, allowing for targeted noise pollution monitoring and control.
Learn more about the technology here.
What role does the NAUTILUS platform play in combining emissions and noise data?
NAUTILUS is a remote sensing data platform that can synchronize emissions and noise data from E-RSD and N-RSD sensors. This combination provides a comprehensive view of both pollutants and noise levels from each vehicle, which is valuable for operators monitoring urban environments.
Watch our animated explainer here.
Can remote sensing devices be used to identify illegally manipulated vehicles?
Yes, RSDs can act as an alert system for the police to detect highly emitting vehicles, which may indicate illegal manipulation, such as the disconnection of AdBlue injection systems in diesel trucks. This application has increased in Europe and supports the enforcement of emission regulations.
Learn more about the identification here.
What are the potential applications of remote sensing technologies in fleet management?
Fleet owners can use RSD technology to monitor the status of their vehicles, ensuring proper operation and identifying any that may be deteriorating or close to failure. Public authorities can also use this technology to audit real emissions from public buses or evaluate emissions from specific vehicle groups like taxis.
Learn more about NEMO’s many applications here.
How can high-emitting vehicles be identified and controlled in urban areas?
By deploying remote sensing devices across a territory, authorities can identify the worst polluting vehicles and take action such as issuing notices of violation, requiring re-inspection, or excluding them from low emission zones.
Learn more about how NEMO empowers LEZ management in cities here.
What are the market prospects for E-RSD and N-RSD technologies?
These technologies are targeted for global application, with different solutions suitable for both advanced economies seeking better mitigation solutions and developing countries aiming to reduce traffic emissions and modernize their infrastructure.
Learn more about the market prospects here.
What are the challenges in commercial adoption of these technologies in Europe?
Regulatory barriers in Europe need to be overcome for these solutions to scale. While there is end-customer interest, the lack of regulation is limiting commercial adoption, as these technologies cannot yet be used to regulate the circulation of high-emitters.
Learn mmore about our policy recommendations here.
What is the expected market growth for automotive exhaust sensing technologies?
The market size for automotive exhaust sensing technologies is expected to grow significantly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30% until 2027, indicating a strong future demand for these solutions.
Learn about hte growth potential here.
How can NEMO's remote sensing solutions be relevant for cities outside of Europe?
NEMO’s remote sensing solutions are relevant for cities outside of Europe due to several universal urban challenges and goals. Here’s how these solutions can be applied globally:
- Air quality improvement: Many cities worldwide are grappling with air pollution. NEMO’s remote sensing technologies can help monitor and analyze emissions from various sources, providing data to implement and enforce air quality standards.
- Noise pollution management: Urban noise is a growing concern. NEMO’s noise remote sensing can help cities monitor noise levels, identify sources of excessive noise, and enforce noise regulations.
- Traffic management: NEMO’s technologies can assist in traffic management by identifying high-emitting vehicles and promoting cleaner transportation methods, contributing to more efficient and environmentally friendly urban mobility.
- Policy development and enforcement: Data from NEMO’s remote sensing can inform policy development, helping cities to craft regulations that target specific pollutants or noise levels. It can also aid in enforcing existing environmental and noise regulations.
- Health and environmental research: The data collected can be used for public health and environmental research, helping cities to understand the impact of pollution and noise on residents and to develop strategies to mitigate these effects.
- Climate change mitigation: By identifying and mitigating sources of greenhouse gas emissions, cities can contribute to global climate change mitigation efforts.
- Smart City initiatives: NEMO’s solutions can be integrated into smart city infrastructure, contributing to the development of connected, intelligent urban environments that continuously monitor and improve living conditions.
- Public engagement and transparency: Making emission and noise data available to the public can increase transparency, raise awareness, and engage citizens in pollution reduction efforts.
- Economic benefits: By reducing pollution, cities can lower healthcare costs associated with pollution-related diseases and create a more attractive environment for tourism and investment.
- Compliance with international standards: Cities looking to comply with international standards, such as those set by the World Health Organization or the United Nations, can use NEMO’s solutions to monitor and report on their progress.
In summary, NEMO’s remote sensing technologies offer versatile applications that can be tailored to the specific environmental, regulatory, and infrastructural needs of cities around the world, not just in Europe. You can learn more about the potential of NEMO and remote sensing technology here.