NEMO’s unique method to detect high-emitting vehicles, and communicate the results to the owners or authorities, recently got scientific recognition. An article outlying the NEMO technology has been accepted to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Sensors Journal. IEEE is the world’s largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity.
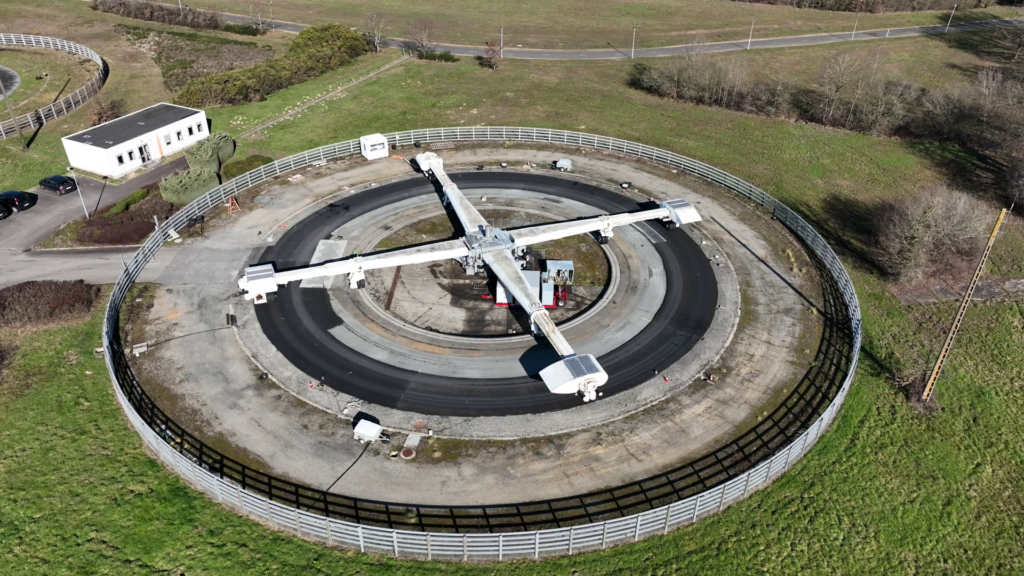
A new paper points to how the NEMO system, an autonomous remote sensing technology, can accurately and cost-effectively identify and classify transgressing noisy and high emitter vehicles. The paper takes you thought the data gathering the modelling process, based on field testing in some European cities. After noise and exhaust emissions data are gathered, the cloud-enabled Nautilus platform is used to evaluate data using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to determine their categorization into different classes of emitters. Continuous testing of different AI models with data from the NEMO demonstration sites in European cities like Rotterdam and the Austrian village Teesdorf, has enabled a development of a unique classification model.
The NEMO model evaluates and accurately classify the vehicles and trains as high, medium, and normal emitters in a dense traffic stream. Additionally, a visualization platform analyses classification results of road pass-by vehicles and trains that can help infrastructure managers and stakeholders to develop policies on the high emitters. Combined with the project’s models for communication to drivers via for example SMS or App, governing bodies and infrastructure managers can affordably identify noisy and high emitter vehicles, including road vehicles and trains, in near real-time. The NEMO solution that can be integrated with already-existing intelligent transportation systems, for example as a tool for enforcement against high emitters in Low-Emission Zones and other sensitive regions.
You can read the full article here.
More of this

